Intel Corp. has changed its roadmap once again and delayed its code-named “Cannonlake” processors to an unknown date. Next year the company will introduce “Kaby Lake” processors made using 14nm FinFET process technology.
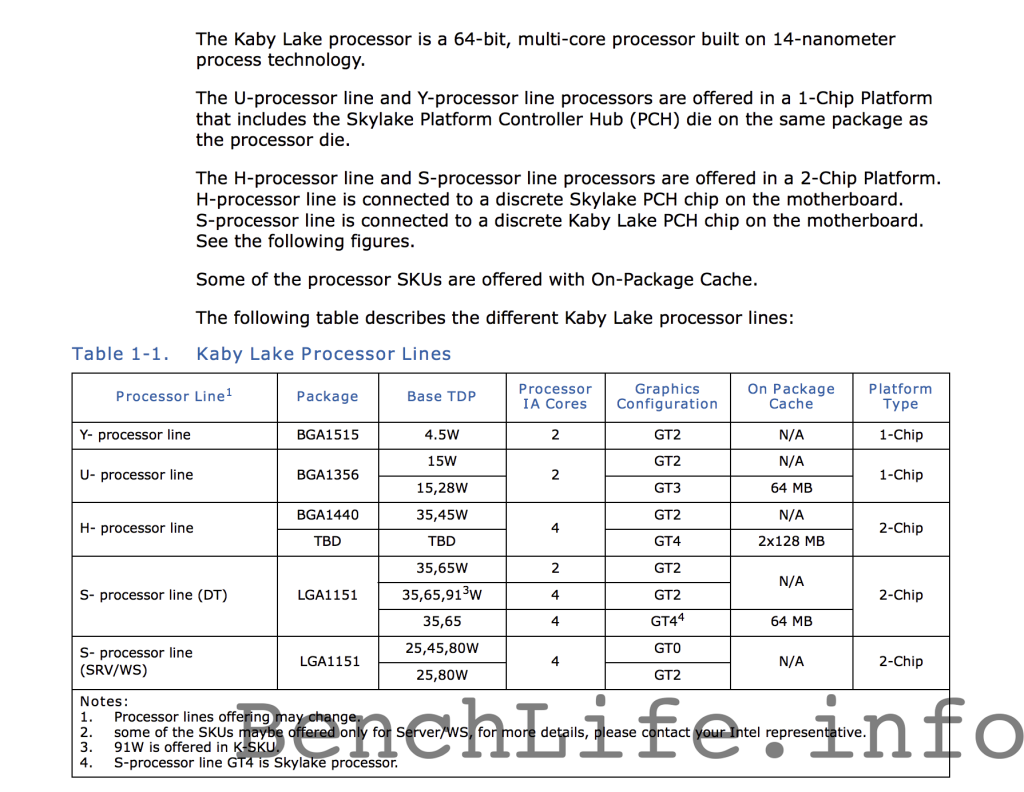
Intel’s “Kaby Lake” processors will feature two or four cores, a new generation integrated graphics engine, a dual-channel memory controller and up to 256MB of on-package cache to speed up graphics workloads. The new chips will address various segments of the market, including mobile and desktop clients, reports BenchLife. The chips will feature thermal design power starting at 4.5W and up to 91W.
Not a lot of information is known about “Kaby Lake” processors. The new chips will be made using 14nm process technology, but it is unclear whether the new central processing units will feature a new micro-architecture. It is also unknown whether the new chips will support AVX-512 instructions.
Intel’s “Kaby Lake” processors for desktops will continue to use LGA1151 packaging and will be drop-in compatible with “Skylake” infrastructure and mainboards based on Intel’s 100-series chipsets. In a bid to make its platforms more competitive, Intel will also add USB 3.1 support to its future core-logic sets.
While the reasons why Intel decided to delay or even cancel “Cannonlake” processors are unknown, it is highly likely that motive behind the change of plans is the postponement of Intel’s 10nm fabrication process.
Intel did not comment on the news-story.
Discuss on our Facebook page, HERE.
KitGuru Says: As it appears, Intel is indeed delaying its 10nm chips to 2017. Apparently, the company’s tick-tock strategy no longer works.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards




02/15 – “Intel vows to ship 10nm chips in early 2017, retracts its promise”
05/15 – “Intel’s 10nm Cannonlake processors due in mid-2016 – leaked roadmap”
06/15 – “Intel’s ‘Kaby Lake’ to replace ‘Skylake’ next year”
LOL. Rumor mill needs to make up its mind.
I think part of the problem is that the 14nm transition was already difficult enough.
Are you sure they are to replace Skylake, and not replace Broadwell but with Skylake’s socket?
Looks like I’m still good with a Haswell@4.7Ghz for a while yet…
so now its officially confirmed that intel has real bad yield issues with 10nm node so they need more time to fix tat…
btw this will really give a nice chance to amd coz after long time we will see intel,amd,ARM on same node…
Kaby Lake = Skylake Refresh
Tick-Tock is done
Moore Law is done
Yeah, it seem we’ll get a new Tick Tack Tock Model. Tack being the refresh with a new stepping and a more mature process.
New rules for new CPU’s : Tick – Refresh – Tock – Refresh
same architecture size and compatible with the same mobo
http://www.anandtech.com/show/9447/intel-10nm-and-kaby-lake
”
Anandtech article says that it will have “key performance enhancements to differentiate it from Skylake”
but intel always change their chipset when it is a tick tock
The laptop H-2 GT4e which was suppose to be Skylake just got split into Kaby, I’d like the native USB 3.1 as well so it”ll be my choice.
Yes! intel changes chipset with tock i.e change in architecture, but they are not doing so with Kaby lake. Because changing motherboard in a year would be big challenge, it might hurt consumers plus zen would be around the corner at that time.
which makes it seem to be more of a refresh, my point has not been contested
You are 100% right its a refresh like devil canyon.
Yeah for a good 5+ years I’d say.
X86 performance really isn’t increasing much at all anymore from Sandy Bridge on up. Haswel to Skylake is 10% or less I believe clock for clock. Yea today’s laptops (except the low voltage ones) are mad fast at regular consumer activities. Just plop in an SSD and it’ll scream even with a lot of bloatware.
Hoping 6 core laptop chips come out eventually.
Dude, thread necro resurrection!!!! 😀 Ended up switching to an X99 system with a 5930k@4.5Ghz. Not a bad boost for encoding etc tbh, and looks like DX12 games will start to utilise the extra cores at some stage B|
Really you got some improvement? From improvement of the integrated GPU?
Single core, most number crunching won’t show much of any improvement I thought.
Well that should last you a good 7 years I wouldn’t doubt 🙂
I was in an Intel roadmap NDA presentation today and they said they’re not on the roadmap. They are focusing more on battery life and Z-height etc and not driving performance like they are on the desktop side of things (e.g., Xeon Processor E5-1650 v2). However they do have Xeons for laptops (“mobile workstations”) now, but still 4-core 🙁
? Kaby Lake won’t get much IPC (instructions per core- per clock) improvement?
Xeon for laptops doesn’t have more performance AFAIK, more security, yes. It’s still a mobile chip.A full fledged Xeon CPU for a workstation laptop is different.
The Desktop and laptop chips are very close in architecture, basically the same I’m pretty sure. So changes in the architecture for performance increases on the desktop Kaby Lake chips will go to the mobile chips too.