Protection Features
Our protection features evaluation methodology is described in detail here.
|
Protection Features |
|
|
OCP |
12V: 49.8A (132.8%), 12.007V |
|
OPP |
666.18W (148.04%) |
|
OTP |
✓ (>120°C @ heatsink area above +12V FETs) |
|
SCP |
12V: ✓ |
|
PWR_OK |
Proper Operation |
|
NLO |
✓ |
|
SIP |
Surge: MOV |
The over power protection is set high, since the unit uses powerful components which with active cooling would easily deliver more than 800W of power. The over current protection is also set high on all rails, with the 5VSB rail holding the crowd with an over 250% OCP triggering point.
The most important protection with a passive power supply is the over temperature protection. We used a heat gun to treat the part of the heatsink that comes in contact with the +12V FETs, since these are usually stressed the most under extreme conditions.
The heatsink's temperature exceeded 120°C with the unit still in operation, so we decided to abort the test. This supply surely has OTP protection, since it is supported by its supervisor IC (SITI PS223), which can be only checked as it seems with the unit opened in order to apply heat to the proper spot. The problem with this testing scenario is though that the NJ450-SXL is only meant to operate with its chassis intact and its heatsinks coming in contact with the major components, and this is why we didn't follow it.
Unfortunately the PSU's NTC thermistor, protecting against large inrush currents, is not supported by a bypass relay which allows for the fast cool down. This means that besides a small percentage of efficiency lost in the NTC thermistor, under some circumstances you may face (even more) increased inrush currents.
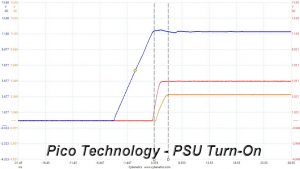
DC Power Sequencing
According to Intel’s most recent Power Supply Design Guide (revision 1.4) the +12V and 5V voltages must be equal or greater than the 3.3V rail’s output at all times, during the power-up and normal operation. For our first measurement, we turn the unit off and switch it back on without any load in any of the rails.
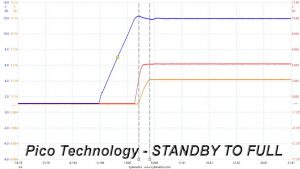
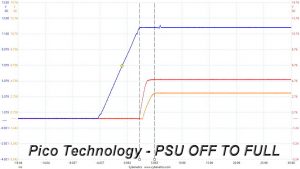
In the second test, we set the PSU to standby mode, dial full load and start it afterwards. In the last test, while the power supply is completely switched off (we cut off the power or switch the supply off through its power switch), we dial full load before restoring power.
No problems here, the 3.3V rail in all cases has lower voltage than the 12V and 5V rails.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards