Test System
- Motherboard: Asus Z97-A/USB 3.1 (ASMedia ASM1142 USB 3.1 ports).
- Processor: Intel Core i7 4790K.
- Memory: 16GB (2x8GB) Corsair Vengeance Pro DDR3.
- System Drive: 120GB SanDisk Extreme SATA SSD.
- Storage Drive: 256GB Plextor M6e M.2 PCIe SSD (for transfer rate testing).
- Operating System: Windows 8.1 64-bit.
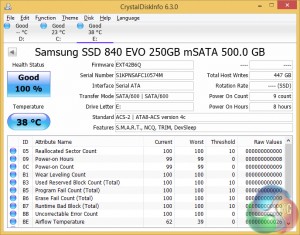
- USB 3.1 Kit: ASMedia-powered USB 3.1 enclosure with two 250GB Samsung 840 EVO mSATA SSDs (RAID 0)
Solely for speed-testing purposes (not for the retail market), Asus provides a USB 3.1-capable enclosure that is filled with a pair of 250GB Samsung 840 EVO mSATA SSDs in RAID 0. The enclosure itself draws power from a micro-USB port and is fed data through a Type-C USB 3.1 connector.
My initial impressions of the reversible Type-C connector are positive. There's no three-time rotation before final insertion (jokingly coined USB superposition), and the linkage force is strong – connector stability was not a problem.
The configuration of Intel PCH-fed USB 3.0 ports and ASM1142-powered USB 3.1 connectors on Asus' motherboard gives us the opportunity to directly compare the new 10Gbps USB solution against its 5Gbps predecessor.
Asus' USB 3.1 Boost software is used throughout testing. The Turbo mode built into the software allows the use of an optimised Bulk-Only Transfer (BOT) architecture which is suggested to provide greater read performance.
Test Results
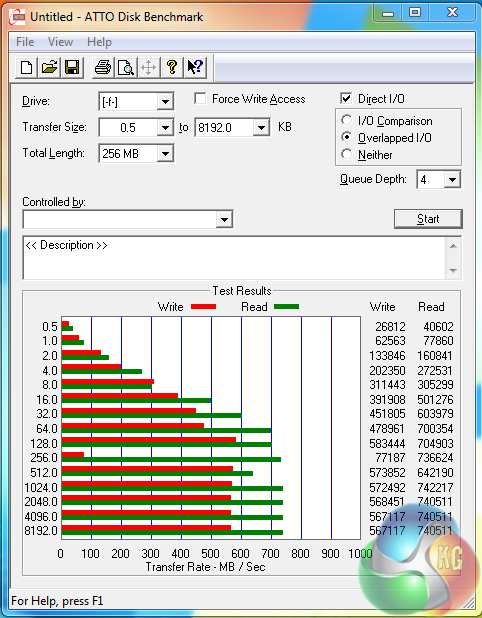
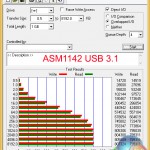
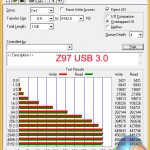
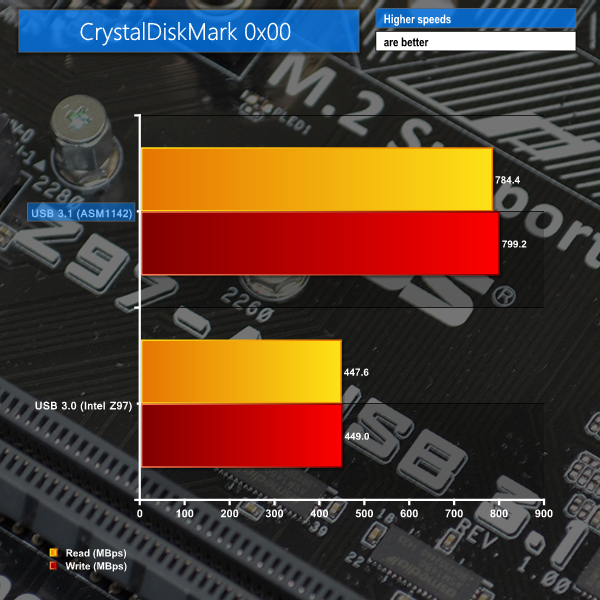
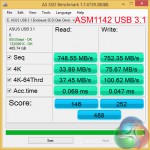
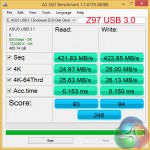
ATTO's simple transfer rate benchmark shows significant improvements (around 80%) when switching from USB 3.0 to USB 3.1.
The symmetrical nature of our USB 3.1 test results imply that around 800MBps is the real-world limit for Asus' PCIe 2.0 x2 solution that is powered by ASMedia's ASM1142 chip. At least that seems to be the case when using chipset-fed PCIe lanes (those from the CPU may be faster).
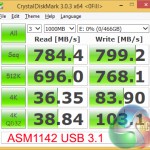
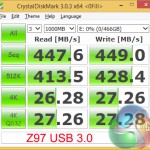
Similar improvements to sequential transfer rates are shown in CrystalDiskMark's incompressible workload (which the Samsung SSDs handle superbly).
Users who transfer large amounts of incompressible data may be able to benefit from speed increases of up to 80%, if their drives are fast enough.
The USB 3.0 ports from Intel's PCH aren't particularly strong performers in 4K testing, so it comes as no surprise that the USB 3.1 connection is significantly faster.
4K write speeds show particular improvement from the newer USB generation, although 4K reads also see a performance boost. The different USB controller manufacturers (ASMedia and Intel) also have an effect on this result.
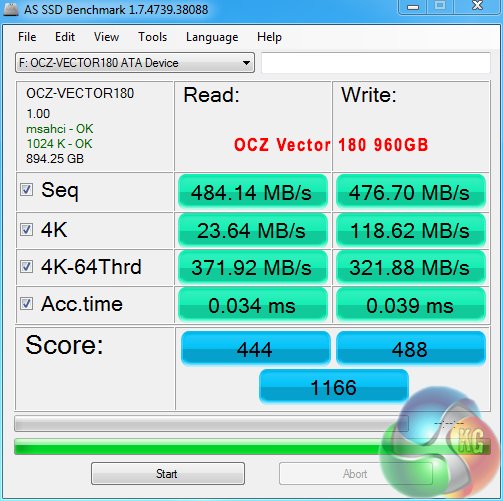
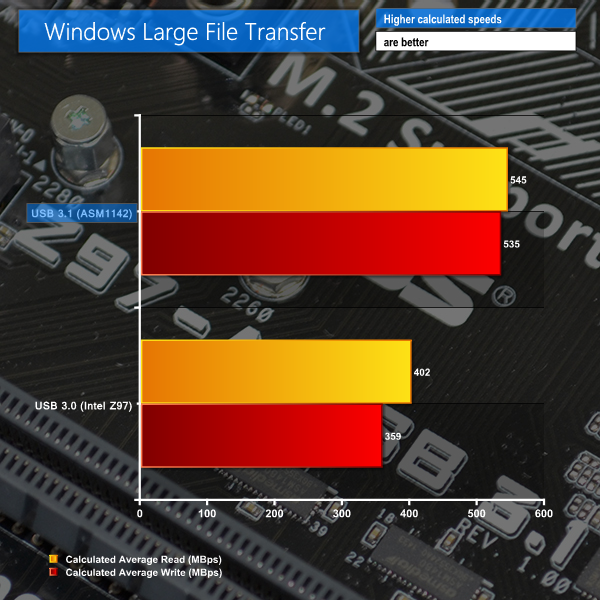
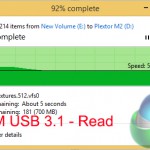
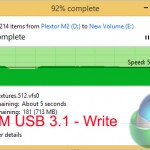
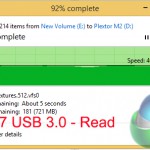
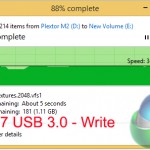
Despite bottlenecks induced by our Plextor M6e SSD (which is actually one of the fastest consumer SSDs available), manual file transfers over USB 3.1 still show significant improvement compared to the USB 3.0 operations.
Writing to the external drive over USB 3.1 showed a ~180MBps (49%) performance increase, while sequential reads were boosted by around 140MBps (36%). Read performance of the USB 3.1 solution was bottlenecked by the 580MBps sequential write speed limit of the Plextor M6e storage drive.
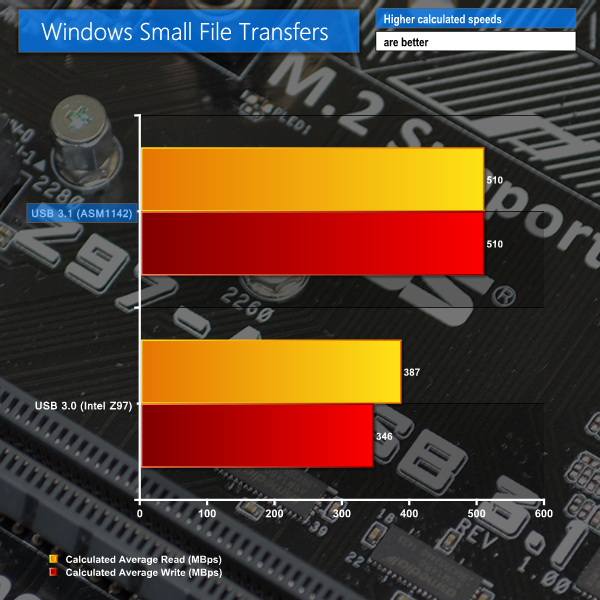
Small mixed file transfers show a similar trend to large sequential read and write operations. Significant improvements to both read and write speeds can be unlocked by utilising USB 3.1.
The throughput capability of a USB 3.1 enclosure partnered with a pair of RAID 0 SSDs requires a fast internal storage drive to make it worthwhile. This speaks volumes for the speed potential of the USB 3.1 interface when comparing it to the realistic performance metrics of internal storage drives (typically less than 600MBps for a single SATA SSD).
Looking back at our USB 3.1 testing using MSI's implementation and a pair of RAID 0 Intel SSDs, we can see that Asus' solution is slightly faster at the upper end of sequential transfers. Most of the variations are tied to usage of Intel RAID 0 SSDs as opposed to Samsung competitors, although Asus' USB 3.1 Boost software looks to be unlocking an extra chunk of performance, especially in sequential read environments.
It is, however, unfair to compare Asus' retail solution against MSI's engineering sample configuration. The point above is primarily for reference purposes, and I would refrain from making any clear recommendations until we compare retail products from all vendors, using identical test hardware (namely the USB 3.1 drives).
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards