We leave the system to idle on the Windows 10 desktop for 5 minutes before taking a power draw reading. For CPU load results we read the power draw while running the Cinebench multi-threaded test as we have found it to push power draw and temperature levels beyond those of AIDA 64 and close to Prime 95 levels. Cinebench has a short run time on high-performance CPUs which influences the validity of the temperature reading, so we run AIDA64 stress test to validate data.
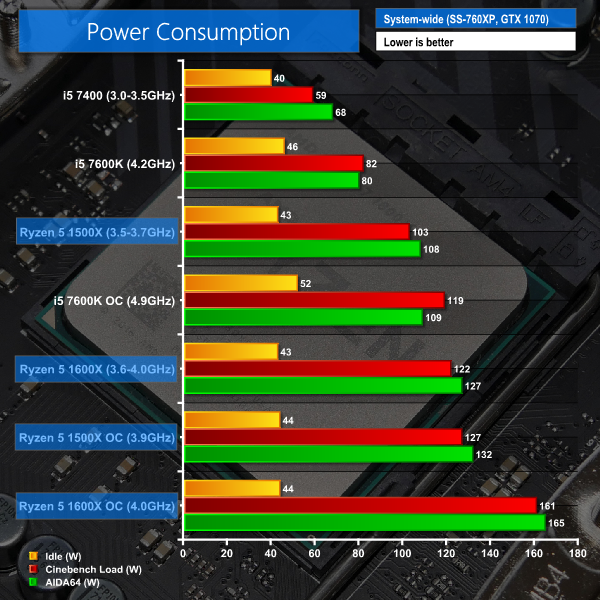
The power consumption of our entire test system (at the wall) is shown in the chart. The same test parameters were used for temperature readings.
Power Consumption
Power draw readings are accurate to around +/- 5W due to fluctuations in the value even at sustained load. We use a Platinum-rated Seasonic 760W PSU and install a GTX 1070 video card that uses very little power.
Given its six physical cores and twelve threads, system-wide power draw from the Ryzen 5 1600X configuration is fine. Our test system pulled around 50% more power for a stock Ryzen 5 1600X compared to a stock Core i5-7600K. That’s an excellent metric given the 78% Cinebench performance lead for the 1600X.
Overclocking adds a very similar amount of power to the Ryzen 5 1600X solution as it does to the Core i5-7600K. Ryzen 5’s flagship demands around 40W (33%) more power than our overclocked i5-7600K configuration but offers 70% higher performance in Cinebench. On a performance-per-Watt basis, the 6C12T Ryzen 5 1600X is vastly superior to Intel’s competing Core i5, based on our Cinebench results.
Temperatures
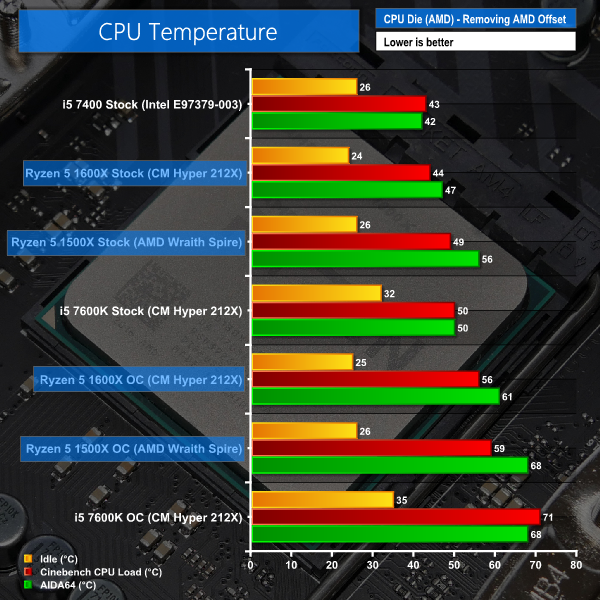
Temperature recordings were taken using the superb, cost-effective Cooler Master Hyper 212X for the Ryzen 5 1600X and the Core i5-7600K. The supplied coolers are used for Ryzen 5 1500X (AMD's Wraith Spire) and Core i5-7400 (Intel E97379-003 with an Aluminium slug).
Each CPU cooler's fan was running at full speed. Ambient temperature was maintained at around 20°C.
No complaints with Ryzen 5 1600X temperatures from us. AMD’s update to Ryzen Master, combined with other software makers’ patches, also help to provide clarity on the +20C offset (that we manually removed to provide the charted temperature readings).
The cost-effective Cooler Master Hyper 212X does a stellar job at keeping the twelve-thread part well-cooled. AMD’s superb heatspreader design puts that of Intel’s solution on Kaby Lake to shame.
Despite drawing less power, the Core i5-7600K runs hotter than Ryzen 5 on a stock-versus-stock and OC-versus-OC basis. Clearly Intel’s implementation of TIM under the Kaby Lake part’s heatspreader is sub-par.
Be sure to check out our sponsors store EKWB here
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards