
In what has seemed like an eternal wait given the 2 years since AMD released its R9 Fury X enthusiast graphics card, the market has grown hungrier and hungrier for competition from the Radeon vendor while Nvidia has been racking up performance crowns and high-end GPU sales. AMD's new Radeon RX Vega series of graphics cards is upon with the aim of creating competition in the high-end space that Nvidia has called its own for many, many months.
Today we are examining the $499/£449 Radeon RX Vega64 graphics card that uses AMD's flagship GPU. The air-cooled variant of the 64 Compute Unit (CU) sits second-fiddle in AMD's product hierarchy to the liquid-cooled variant of the same GPU. AMD has put Nvidia's roughly £500 GTX 1080 firmly in the sights of Vega64.
Successive leaks and the launch of AMD's prosumer Vega Frontier Edition back in June have made almost all Vega details a known entity by this point. A very tight review schedule means that will encourage you to read our previous content regarding the specific features for Radeon RX Vega, including the ‘pack' bundles in which the cards are also being sold (HERE and HERE).
In short, AMD is aiming to make Vega64 an appealing option to high-refresh rate 1080P and 1440P gamers who also want to leverage the widened desirable FPS range of FreeSync monitors. Do not expect Vega to give borderline single-GPU 4K60 performance that requires the use of Nvidia's GTX 1080 Ti or Titan Xp in AAA games. That's not on the cards (excuse the pun) for Vega unless image quality is reduced significantly at 4K.
| GPU | AMD RX Vega64 Liquid |
AMD RX Vega64 Air |
AMD RX Vega56 | Nvidia GTX 1070 | Nvidia GTX 1080 | Nvidia GTX 1080 Ti |
| GPU Name | Vega 10 | Vega 10 | Vega 10 | GP104 | GP104 | GP102 |
| GPU Cores | 4096 | 4096 | 3584 | 1920 | 2560 | 3584 |
| Base Clock | 1406MHz | 1247MHz | 1156MHz | 1506 MHz | 1607 MHz | 1480 MHz |
| GPU Boost Clock | 1677MHz (Avg) 1750MHz (Max) | 1546MHz (Avg) 1630MHz (Max) | 1471MHz (Avg) 1590MHz (Max) | 1683 MHz | 1733 MHz | 1582 MHz |
| Total Video Memory | 8GB HBM2 | 8GB HBM2 | 8GB HBM2 | 8GB GDDR5 | 8GB GDDR5X | 11GB GDDR5X |
| Texture Units | 256 | 256 | 256 | 120 | 160 | 224 |
| Texture fill rate | 429.3 GT/s | 395.8 GT/s | 330.0 GT/s | 180.7 GT/s | 257.1 GT/s | 331.5 GT/s |
| Memory Bit Rate |
1.89 Gbps effective | 1.89 Gbps effective | 1.60 Gbps effective | 8 Gbps effective | 10 Gbps effective | 11 Gbps effective |
| Memory Bandwidth | 484 GB/s | 484 GB/s | 410 GB/s | 256.3 GB/s | 320 GB/s | 484 GB/s |
| Bus Width | 2048-bit | 2048-bit | 2048-bit | 256-bit | 256-bit | 352-bit |
| ROPs | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 88 |
| Manufacturing Process | 14nm | 14nm | 14nm | 16nm | 16nm | 16nm |
| TDP | 345 W | 295 W | 210 W | 150 W | 180 W | 250 W |
| Power Connector(s) | 2x 8-pin | 2x 8-pin | 2x 8-pin | 1x 8-pin | 1x 8-pin | 1x 6-pin + 1×8-pin |
| Launch MSRP | $699 (Radeon Aqua Pack) | $499 | $399 | $449 (FE) | $699 (FE) | $699 |
| UK Starting Price (Aug 2017) |
£639 Suggested (Radeon Aqua Pack)
£670+ Current |
£450 Suggested
£550+ Current |
Estimated Approx. £360 | Approx. £350-380 (limited stock) | Approx. £490 | Approx. £670 |
AMD equips Vega with its potential ‘wildcard' compared to Nvidia – 8GB of HBM2 VRAM clocked at 1.89Gbps effective that sits on a massive 2048-bit to give 484GBps of memory bandwidth. We have seen HBM used in the past on AMD's Fiji GPU but the 4GB capacity limit was a severe drawback for an enthusiast card in today's high-resolution market. HBM2 addresses the capacity concern of version 1 by making 8GB capacities on the Vega GPUs a possibility. Two stacks sit next to the GPU on the interposer to create a streamlined single package for the GPU and 8GB of HBM2.
You may hear this memory referred to as a ‘High-Bandwidth Cache (HBC)', alongside the ‘High-Bandwidth Cache Controller (HBCC)'. AMD's use of the word ‘cache' is a reference to the card's ability to access system RAM to make a wider pool of memory available to the GPU. So the ‘cache' term bears no significant reference to the 8GB of dedicated HBM2 VRAM in itself. If, for example, you have a large data set that fills the 8GB of dedicated HBM2 memory, a quantity of system memory can be allocated to the GPU to create a larger available pool.
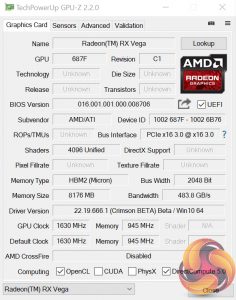
Looking at raw horsepower, AMD's RX Vega64 Air is built around a 486mm2 14nm manufactured ‘Vega 10' GPU consisting of 12.5 Billion transistors. 64 Next-Gen CUs create 4096 stream processors that can clock up to 1630MHz on the air card to give peak single-precision performance of around 13 TFLOPS. Half precision performance sits more in the mid-20s TFLOPS range, allowing (theoretically) higher performance in certain scenarios for upcoming games that have been touted to support FP16 Rapid Pack Math, such as Wolfenstein 2 and Far Cry 5.
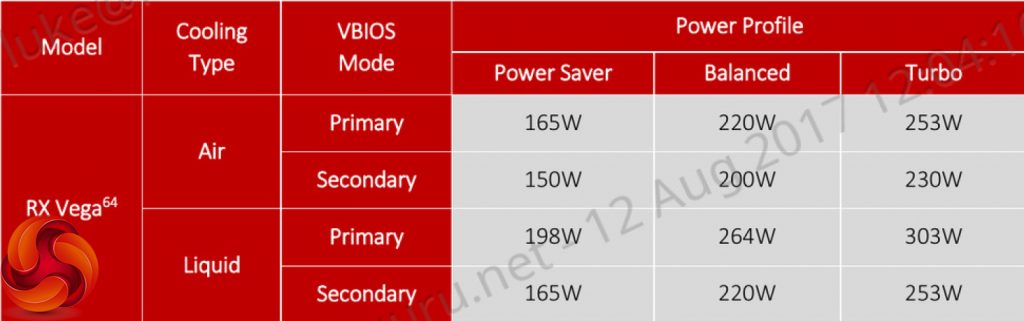
AMD makes different power states available to RX Vega64 in its WattMan software. These different modes are easily selectable with just a few clicks. AMD's goal here seems to be covering both bases with Vega64. There is a power saving mode to allow the card to operate more efficiently and quietly at a TDP and frequency where the GPU sits more favourably on its efficiency curve. Then there's the ‘balls-to-the-wall‘ Turbo mode that throws power draw and noise output cares out of the window by allowing the GPU to clock up to a point that is beyond its smart efficiency range, all in the name of performance.
Kudos to AMD for including adjustable modes. These give extra control to the gamer and are a feature that is definitely worthwhile in an easily-accessible software setting location. However, some enthusiasts may look at this as acceptance by AMD that the vendor cannot compete with Nvidia's efficiency while offering the same performance levels, hence the need for a ‘Turbo' mode that significantly increases power available to the GPU.
Power efficiency is an area where AMD still lags behind Nvidia (based on the assumption that RX Vega64 will not offer GTX 1080 Ti-beating performance). The air-cooled card is rated at a hefty 295W while the liquid-cooled version ups that to 345W. Vega64 requires dual 8-pin power connectors which means that it will not feature the PCI-e logo. RX Vega64 Air's box suggests a 750W PSU whereas 500W is Nvidia's recommendation for the GTX 1080.
Speaking of boost clocks, the Vega64 Air is rated at up to 1630MHz but, spoiler alert, it rarely stays at that speed. Unlike Nvidia's GPUs that state a boost clock and spend most of their time operating higher than it, AMD's higher quoted boost clock is the maximum frequency for the GPU.The other figure you may hear (1546MHz in the case of Vega64 Air) is the average boost clock, as claimed by AMD, based on several workloads.
We saw 1630MHz being hit for short periods of time, primarily in less-demanding use cases (1080P gaming), before throttling of a thermal or power nature reduced the figure to around 1546MHz or 1401MHz. AMD's 1630MHz maximum quote and 1546MHz average quote seem fair but further testing will confirm that.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards




Has anyone found a store actually selling these in the UK yet? Release date is today, but can’t find anything at overclockers.co.uk, amazon.co.uk, etc.
What a shocking bad cooler. Will wait on some partner cards before making a decision. Power consumption looks dire too. 🙁
Scan and overclockers got some stock
1900 MHz? How much power will then need to be delivered to it 😀
kinda disapointed because to me, this VEGA won’t make my fury X obsolete, delivery 95 FPS 1080p on Deus ex, the fury delivery 85 fps on 1080p, to me at least isn’t a great evolution :/
The prices on Overclockers for the Vega 64 is £548.99 for the cheapest and £599 for the special edition..though not in stock…The cheapest GTX 1080 reference on Overclockers is £449.99 and in stock.. a £100 price difference.. It’s got get to the price of the GTX…please!
A factory overclocked GTX 1080 G1 gaming by Gigabyte is only 519USD on Amazon.
I’m sure you could find cards costing 499 by other vendors
Vega 64 even in 499 isn’t worth it when you consider the price to performance to TDP.
GTX 1080 is a better buy if you care only for gaming performance and TDP….unless you want mining in which Vega 64 might be better.
I get what you’re saying, but it’s not meant to be a 1080p-optimised card
It’s hitting 1440p very well, but is still lagging in 4K. It’s an upgrade compared to Fury X, and probably noticeably in games, but it probably won’t blow you away like a 1080TI would. It’s cheaper than the TI, but still disappointing that AMD isn’t going after high end anymore.
I will wait till board partners and custom bioses so I can OC this beast. A Vega 64 LC board with a EK waterblock in my loop and 2 bioses would be just awesome. I just hope the drivers arrive and enable primitive shaders, Rapid packed math and fix the HBCC. I won’t treat these benchmarks as final and would take them with a grain of salt. Besides, you are NOT playing the games, you are using the in-game benchmarks which are INACCURATE, so ALL the KitGuru benchmarking are UNRELIABLE!!!!
No one in their right mind should buy a Vega 64 at 1080 prices when you consider its gaming performance and TDP.
Lol you are obsessed with TDP. No gamer should care. Can you give it enough power? Can you keep it cool?
Your arguing a point that means little since this cards power delivery was build almost perfectly.
You should not be as you don`t know what the card will do once its optimized for the game. Once more Dirt 4 changed 1 AA setting and it went from neck and neck with 1070 to smashing it by 24%. Also when I look at the games it struggles in they are mainly past there prime, like GTA 5 and if someone tweak cache settings this Vega will take off like a rocket.
The one thing HBM simply cannot be argued about is how insanely powerful it is calling massive textures as well as limiting the low frame dips.
I notice micro stutters and frame dips 100x more than a 10 FPS difference past 60 TBH.
And I am really going for that. Hopefully it blows the doors off the current lows.
Power doesnt matter as much on here because normally we equate tons of power with heat. But this VRM is at the realistic limit almost at 91.5%
Pls link it. I have been looking for a long time twice daily, and because Nvidia slacked when miners first appeared they have been wiped out.
Also why should gamers care about TDP at all? Its the miners who should. Gamers in general have much higher PSUs than normal as well as spend tons on parts they cant even use all the way “Hello 1080”.
If anyone is using the 1080 for 1080P at any level the 1080 is a massive waste. And this is where the 56 Vega is so great, it blurs the 1070/1080 line.
Hell the best bang for buck card that is worth it as much as a 1070 is the 1050TI for its price.
It has always been said the 970/1070 lines are the high sweet spot while 960/1060 was low sweet spot.
TDP only matters if the VRM is iffy. Vega has the best VRM made in a while and so even with huge power input it doesn’t get limited by thermals, its limited by power, which once more better for gamers.
I am going to either get a 1070 or Vega to replace my 970. Basically the reason im leaning hard Vega now is Free Sync. Running 100 FPS is a odd but very nice spot in games and Gsyncs are just insanely priced.
yeah, I only sad that’s VEGA isn’t make Fury X obsolet, worth it more get a second fury x than a new VEGA…